
Project
A Project is the core workspace in the system. It represents an isolated environment where teams manage builds, test cases, test campaign, APIs, automation rules, and execution history — all under a single access and security boundary.
Each project has its own members, permissions, current build, and execution context, ensuring complete separation between different products or clients.
Why it matters
-
Isolation by design
Each project is fully separated, preventing data leakage between teams, clients, or environments. -
Single source of truth
All testing artifacts (cases, plans, APIs, executions, automation) live under one controlled scope. -
Permission-driven access
Visibility and actions are strictly enforced based on project type and user role.
When to use it
-
Multi-product environments
When managing multiple applications, games, or services in parallel. -
Client-based QA setups
When each client requires isolated data, reports, and access control. -
Long-running test programs
When tracking builds, executions, and history over time is critical.
Core concepts
-
Project – The top-level container that defines scope, ownership, visibility, and access control.
All data, actions, and permissions are evaluated within the project boundary. -
Project Type – Defines who can see and interact with the project:
-
Private: accessible only to the owner and administrators
-
Team: accessible to invited members
-
Public: visible based on role and system rules
-
-
Project Membership – Explicit relationship between users and the project, defining who is allowed to view or manage it.
-
Current Project – The active project selected by the user.
All operations (create, edit, run, delete) are performed only inside this context. -
Build Context – The currently active build (version, platform) attached to the project and used during executions and reporting.
How it works
-
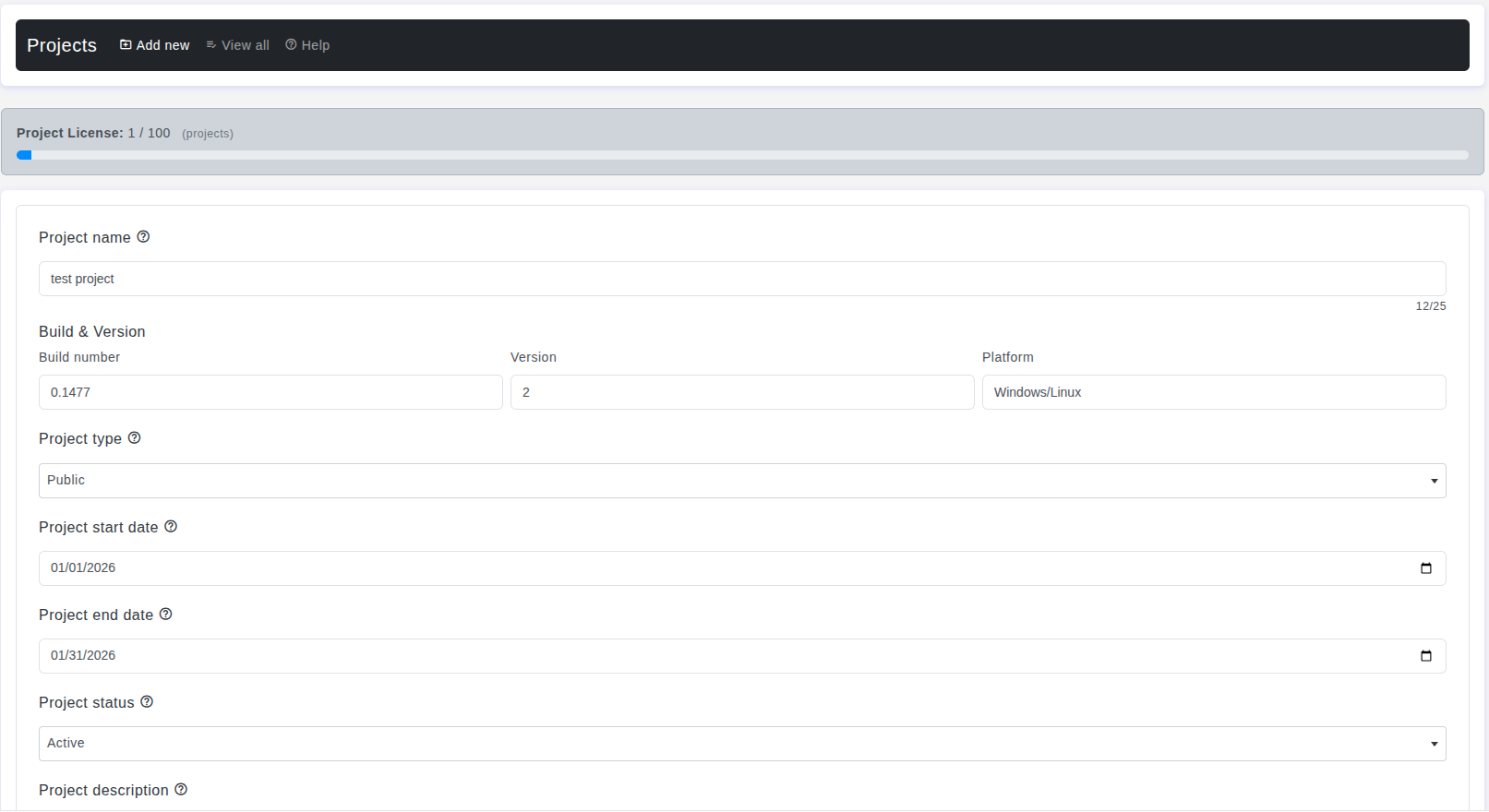
Create a project
Define project name, visibility (Private / Team / Public), dates, and initial team members. -
Activate a project
The selected project becomes the current project for the user session. -
Manage builds
Add and activate builds (build number, version, platform) to control execution context. -
Operate inside the scope
All test cases, plans, APIs, automation, and logs are automatically linked to the active project.
How to use it
Step 1: Create a project
Go to the Projects page and create a new project.
Optionally add an initial build and invite team members.
Step 2: Activate the project
Select the project to make it your current working context.
All actions will now apply only to this project.
Step 3: Add testing assets
Create test cases, group them into test campaign, define APIs, and configure automation rules.
Step 4: Execute and track
Run tests manually, on the server, or via Smart Agent — executions and logs are stored per project.
Best practices
-
Use one project per product or client
Avoid mixing unrelated systems inside the same project. -
Always set and maintain the active build
This ensures accurate execution context and reporting. -
Limit visibility intentionally
Prefer Private or Team projects unless public access is truly required.
Common mistakes
❌ Using one project for multiple clients
✔ Create a separate project for each client or environment.
❌ Forgetting to activate the correct project
✔ Always verify the current project before editing or executing tests.
Security & permissions
-
Strict access control
Access is enforced based on project type (Private / Team / Public) and user role. -
Current project validation
Users lose access automatically if project visibility or membership changes. -
Audit and execution isolation
Logs, executions, and share access are scoped per project to prevent cross-project exposure.
Related documentation
-
Test Cases overview
-
Test Campaign overview
-
Builds & execution context